Tree Biomass Estimation in Karst Forest of West Papua, Indonesia
Abstract
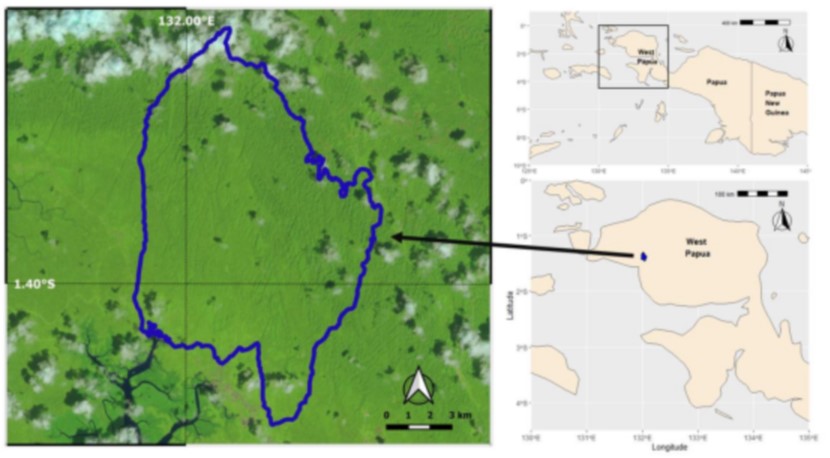
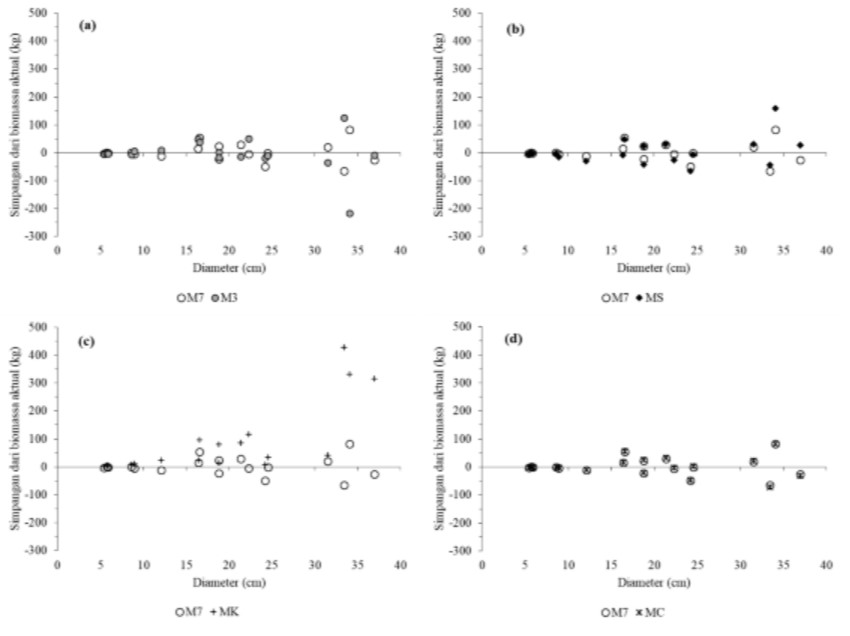
Indonesia is estimated to have 14,5 million hectares of karst areas. The characteristic of karst vegetation is specific, one of which is the dominance of small trees. With all of the potency, their vegetation acts as a significant carbon sequester and store it in biomass. This study aims to estimate and discuss biomass estimation in the karst forest within the Nature Recreational Park of Beriat, a protected area in South Sorong, West Papua. A total of 28 plots were made in the forest using the purposive random sampling method. Tree biomass (DBH ≥10 cm) was estimated using five different allometric equations. The results showed that the biomass was estimated at ca. 264 Mg ha-1 (95 % CI: 135-454 Mg ha-1). While small trees (DBH 10 – 30 cm) only contribute 30 % of the total biomass, about 38 % of the biomass is the contribution of large trees (DBH >50 cm), where Pometia pinnata contributes ca. 39 % of the biomass at plot-level. The use of various allometric equations results in different biomass estimates and biases with deviations ranged from -14.78 % to +17.02 % compared to the reference equation. Therefore, the selection of allometric equations used must be considered carefully to reduce uncertainties in biomass estimation.
Copyright (c) 2021 Jurnal Wasian

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright and License
All articles published in Wasian Journal are the property of the authors. By submitting an article to Wasian Journal, authors agree to the following terms:
-
Copyright Ownership: The author(s) retain copyright and full publishing rights without restrictions. Authors grant the journal the right to publish the work first and to distribute it as open access under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
-
Licensing: Articles published in Wasian Journal are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). This license allows others to share, copy, and redistribute the material in any medium or format, and adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially, provided that proper credit is given to the original author(s) and the source of the material

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. -
Author's Rights: Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges and greater citation of published work.
-
Third-Party Content: If your article contains material (e.g., images, tables, or figures) for which you do not hold copyright, you must obtain permission from the copyright holder to use the material in your article. This permission must include the right for you to grant the journal the rights described above.
-
Reprints and Distribution: Authors have the right to distribute the final published version of their work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), provided that the original publication in Wasian Journal is acknowledged.
For the reader you are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format for any purpose, even commercially.
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit , provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made . You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation .
No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rightsmay limit how you use the material.