Ethnic Influence Against Land Use Patterns and Its Contribution to Community Income in The Aketajawe Lolobata National Park (Pengaruh Etnis Terhadap Pola Pemanfaatan Lahan Dan Kontribusinya Bagi Pendapatan Masyarakat Di Taman Nasional Aketajawe Lolobata)
Abstract
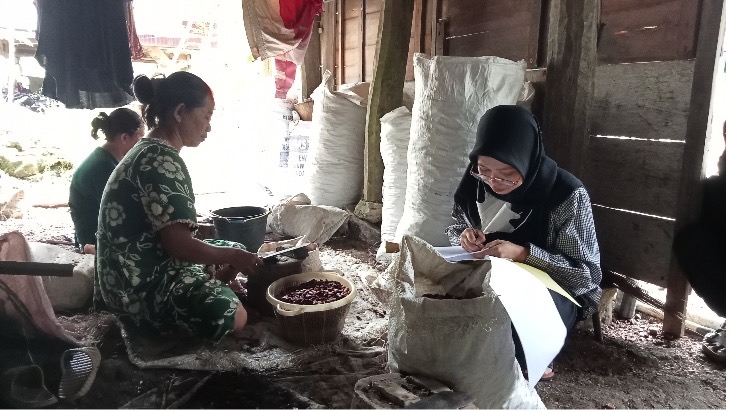
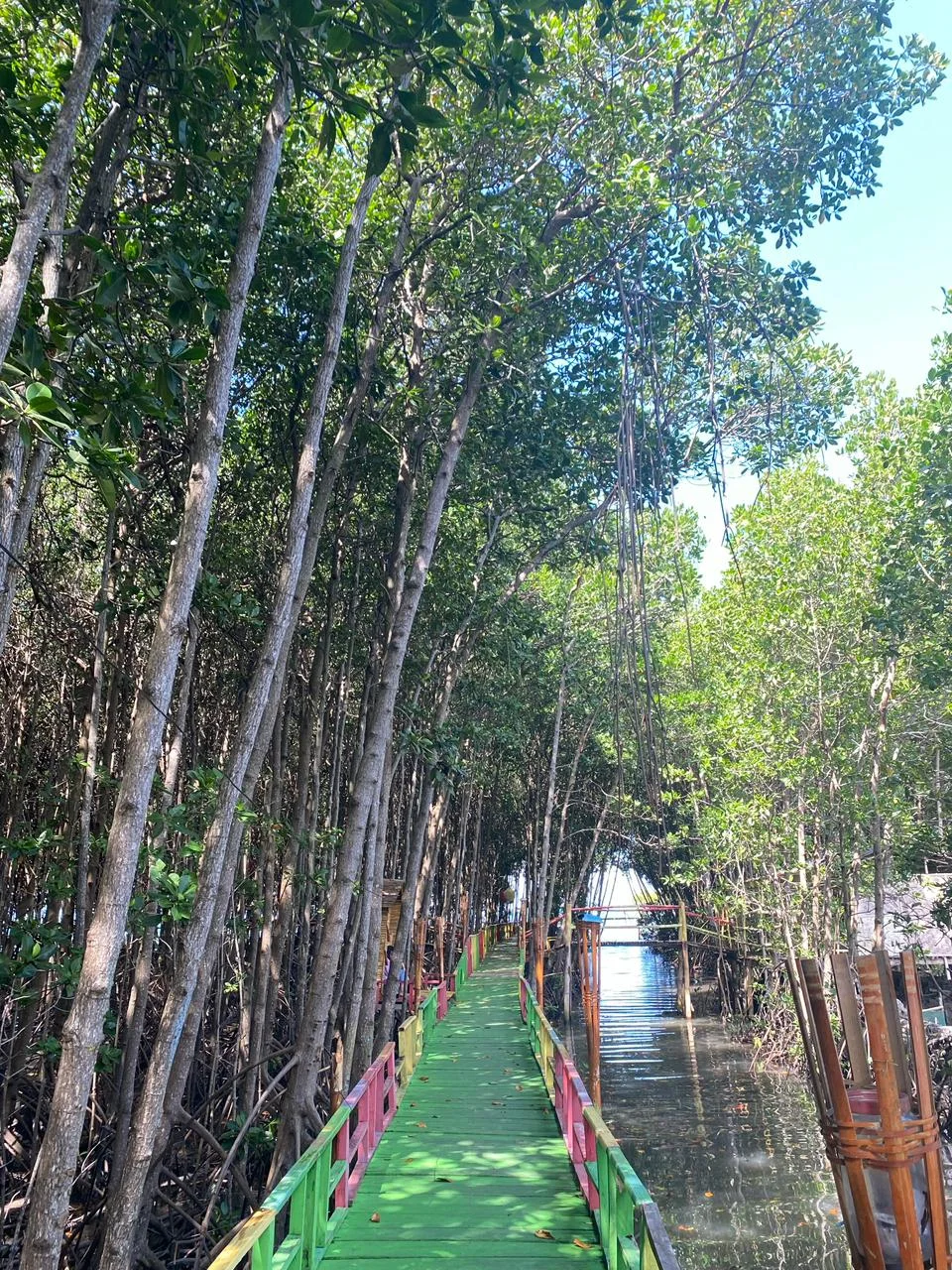
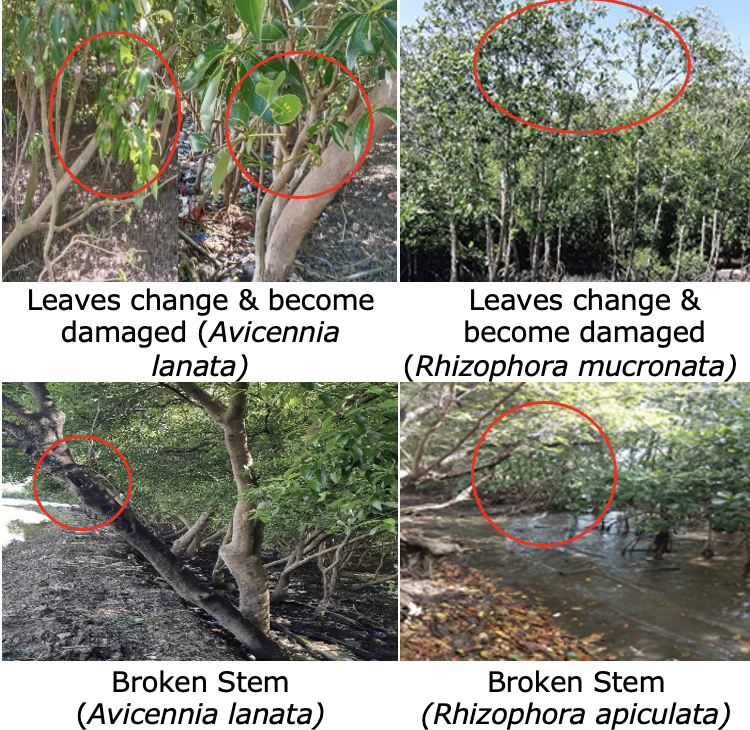
Buffer zone management is an integrated practice of managing forest and agriculture land based on biophysical nature of region and social-culture combination to obtain an optimum forest and agriculture products that support local livelihood economy. The study was to identify the community land use patterns that shapes the buffer zone of Aketajawe Lolobata National Park particularly at Aketajawe block. Sampling villages were determined by stratification based on the distance from the National Park boundary which varied between <3,3-5, and > 5 km. The purposive random sampling was chosen 82 respondents to be interviewed. Land use pattern which applied by communities were divided into six groups according to cultivated commodities i.e. community forest, mixed garden, monoculture garden, intercropping garden, horticulture and rice fields. The differences of these patterns were influenced by background and origin of communities. The indigenous people of Halmahera island used their land as mixed garden while the settler used theirs as rice field and horticulture. Based on the land cover quality, mixed garden pattern was more similar to forest vegetation than another pattern. Rice field pattern gave the largest economic contribution while community forest gave the lowest contribution to the farmer’s income.
##submission.copyrightStatement##
##submission.license.cc.by-nc4.footer##Copyright and License
All articles published in Wasian Journal are the property of the authors. By submitting an article to Wasian Journal, authors agree to the following terms:
-
Copyright Ownership: The author(s) retain copyright and full publishing rights without restrictions. Authors grant the journal the right to publish the work first and to distribute it as open access under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
-
Licensing: Articles published in Wasian Journal are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). This license allows others to share, copy, and redistribute the material in any medium or format, and adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially, provided that proper credit is given to the original author(s) and the source of the material

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. -
Author's Rights: Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges and greater citation of published work.
-
Third-Party Content: If your article contains material (e.g., images, tables, or figures) for which you do not hold copyright, you must obtain permission from the copyright holder to use the material in your article. This permission must include the right for you to grant the journal the rights described above.
-
Reprints and Distribution: Authors have the right to distribute the final published version of their work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), provided that the original publication in Wasian Journal is acknowledged.
For the reader you are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format for any purpose, even commercially.
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit , provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made . You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation .
No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rightsmay limit how you use the material.
##plugins.generic.recommendByAuthor.heading##
- Margaretta Christita Margaretta, Iwanuddin Iwanuddin Iwanuddin , Yermias Kafiar Yermias, Supratman Tabba Supratman , Identification of Water Bacteria from Nickel Post Mining in East Halmahera , Jurnal Wasian: 卷 5 期 1 (2018): June
- Supratman Tabba Supratman , Lis Nurrani Nurrani, Distribution of Avifauna in Aketajawe Lolobata National Park Based on Zone and Land Cover Typology , Jurnal Wasian: 卷 3 期 1 (2016): June
- Supratman Tabba Supratman, Nurlita Indah Wahyuni Nurlita, Hendra Susanto Mokodompit Hendra , Composition and Structure of Tiwoho Mangrove Vegetation at Bunaken National Parkional Park (Komposisi Dan Struktur Vegetasi Mangrove Tiwoho di Kawasan Taman Nasional Bunaken) , Jurnal Wasian: 卷 2 期 2 (2015): December
- Lis Nurrani Lis Nurrani, M Bismark Bismark, Supratman Tabba Supratman , Institution and Communities Participation in the Conservation Of Mangrove/Case Study in Tiwoho Village, North Province , Jurnal Wasian: 卷 2 期 1 (2015): March