The Effect of Weaning Tecnique to Survival Rate and Height Growth of Nyamplung (Calophyllum inophyllum) Plant
Abstract
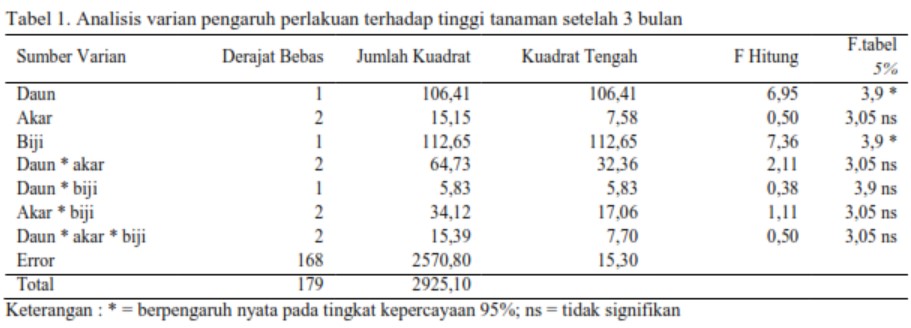
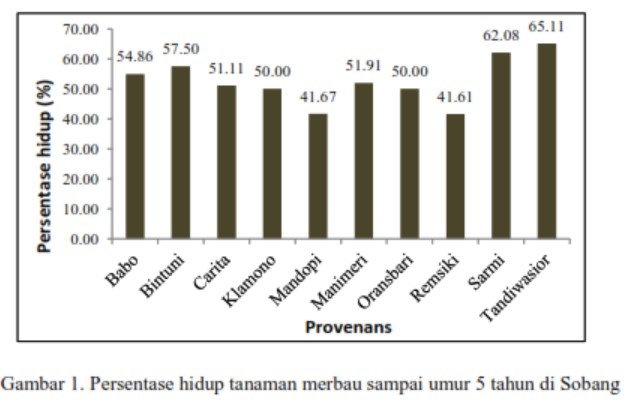
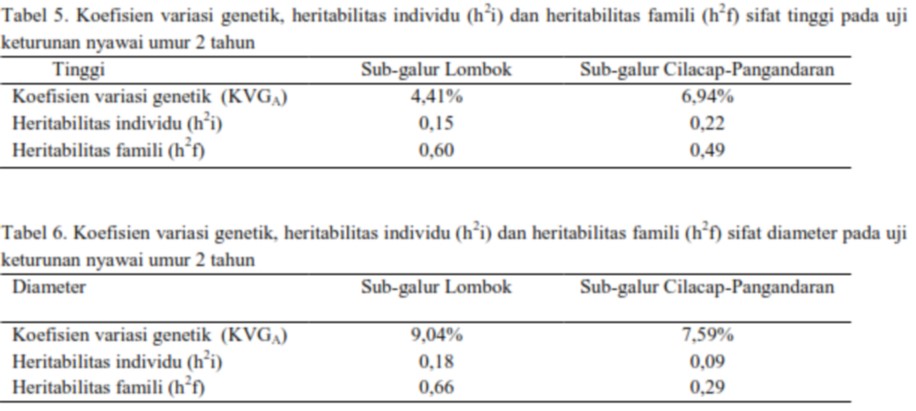
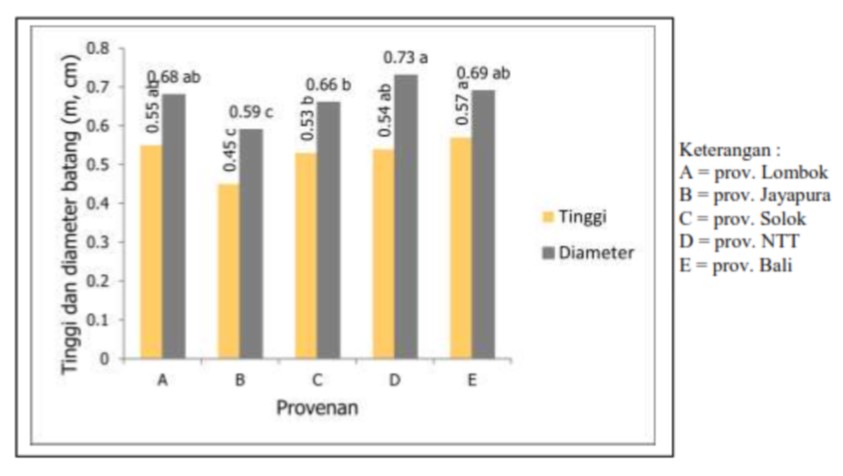
Technical rehabilitation planning of BPDAS Tondano on coastal area has reached 10,000 hectares, thus require many seedlings. Nyamplung has potential as rehabilitation plant in coastal at the same time it can support national demand of biofuel. However the nurseries of nyamplung in North Sulawesi are not optimal and need appropriate information of weaning method. This research used completely randomized design with three treatment factors, namely 1) Cutting the leaves consist of two levels ie D1 (pair leaves) and D2 (intact leaf); 2) Cutting intact seeds, consists of two levels i.e B1 (removed seed) and B2 (intact seeds); and 3) Cutting the roots lenght consist of three levels i.e A1 (5 cm), A2 (10 cm) and A3 (15 cm). There were 180 seedlings taken from seed that germinated using cocopeat media. Results of variance analysis showed that the applied treatment only affect the heigth growth. The survival rate is not affected by all treatments or in the other words survival rate reached 100 %. The treatments on leaves and seeds gave significant effect, on the contrary with root treatment. The treatment of intact leaf (D2) and intact seeds (B2) produced the best height growth responses i.e 4.60 cm and 4.63 cm.
Copyright (c) 2017 Jurnal Wasian

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright and License
All articles published in Wasian Journal are the property of the authors. By submitting an article to Wasian Journal, authors agree to the following terms:
-
Copyright Ownership: The author(s) retain copyright and full publishing rights without restrictions. Authors grant the journal the right to publish the work first and to distribute it as open access under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
-
Licensing: Articles published in Wasian Journal are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). This license allows others to share, copy, and redistribute the material in any medium or format, and adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially, provided that proper credit is given to the original author(s) and the source of the material

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. -
Author's Rights: Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges and greater citation of published work.
-
Third-Party Content: If your article contains material (e.g., images, tables, or figures) for which you do not hold copyright, you must obtain permission from the copyright holder to use the material in your article. This permission must include the right for you to grant the journal the rights described above.
-
Reprints and Distribution: Authors have the right to distribute the final published version of their work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), provided that the original publication in Wasian Journal is acknowledged.
For the reader you are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format for any purpose, even commercially.
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit , provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made . You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation .
No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rightsmay limit how you use the material.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Arif Irawan, Kristian Mairi, Sulistya Ekawati, Analysis Of Tenurial Conflict In Production Forest Management Unit (Pfmu) Model Poiga , Jurnal Wasian: Vol. 3 No. 2 (2016): December
- Ady Suryawan, Mangrove Rehabilitation at Alo Beach (Karakelang Islands, Talaud) Using Propagul of Rhizophora mucronata Lamk , Jurnal Wasian: Vol. 4 No. 2 (2017): December
- Arif Irawan, Hanif Nurul Hidayah, Shade Effect on Growth and Quality of Cempaka Wasian Seedling (Magnolia tsiampaca (Miq.) Dandy) in Nursery , Jurnal Wasian: Vol. 4 No. 1 (2017): June