Correlation of Morphological Characteristics of Nyamplung Seedling (Calophyllum inophyllum L) with The Performance at Field Condition
Abstract
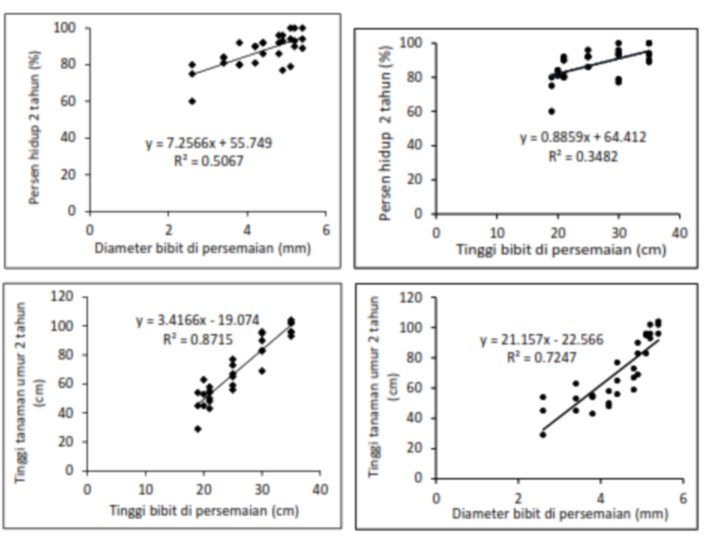
The aim of this research is to assess the correlation of morphological characteristics of nyamplung seedling (Calophyllum inophyllum L) on field growth of two years age after outplanting in Parungpanjang, Bogor. Three seedlots collected from Carita, Pangandaran and Purworejo were grown in seedbeds with different ages (four months and six months). The seedlings are mixed and grouped according to their height and root collar diameter. Each group of seedlings is divided into 5 height classes and each class is divided into two diameter classes, so there are 10 classes of seed morphology. The parameters of seedling were observed on sturdirness quotient, dry weight, root length, shoot-root ratio, and number of leaves. The seedlings were planted in randomized completely block design (three seeds origins, 10 morphological class, three blocks, 30 seedlings per block). Seedling survival, height, and root collar diameter growth were assessed on two years after outplanting. The result showed that morphological classification affected on seedling survival, height and root collar diameter growth. Seedling height and root collar diameter were significantly correlated with other parameters and also with field growth. Two-year-old Nyamplung on field can grow significantly if we use seedling with a height above 31 cm and a diameter more than 5.1 mm. In addition, the ratio of height and diameter and seed quality index are become important consideration in seed selection.
Copyright (c) 2019 Jurnal Wasian

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright and License
All articles published in Wasian Journal are the property of the authors. By submitting an article to Wasian Journal, authors agree to the following terms:
-
Copyright Ownership: The author(s) retain copyright and full publishing rights without restrictions. Authors grant the journal the right to publish the work first and to distribute it as open access under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
-
Licensing: Articles published in Wasian Journal are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). This license allows others to share, copy, and redistribute the material in any medium or format, and adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially, provided that proper credit is given to the original author(s) and the source of the material

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. -
Author's Rights: Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges and greater citation of published work.
-
Third-Party Content: If your article contains material (e.g., images, tables, or figures) for which you do not hold copyright, you must obtain permission from the copyright holder to use the material in your article. This permission must include the right for you to grant the journal the rights described above.
-
Reprints and Distribution: Authors have the right to distribute the final published version of their work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), provided that the original publication in Wasian Journal is acknowledged.
For the reader you are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format for any purpose, even commercially.
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit , provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made . You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation .
No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rightsmay limit how you use the material.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Iskandar Z Siregar, Riki Ramdhani, Evayusvita Rustam, Dede J Sudrajat, The Effect of Invigoration Using Polyethylene Glycol And Ultra Fine Bubble on Improving of Sengon Seeds (Falcataria Moluccana Miq.) Quality After Two Years Storage , Jurnal Wasian: Vol. 8 No. 2 (2021): December