The Potency of Some Wild Edible Mushrooms with Economic Value in Belitong Island, The Province of Bangka Belitung
Abstract
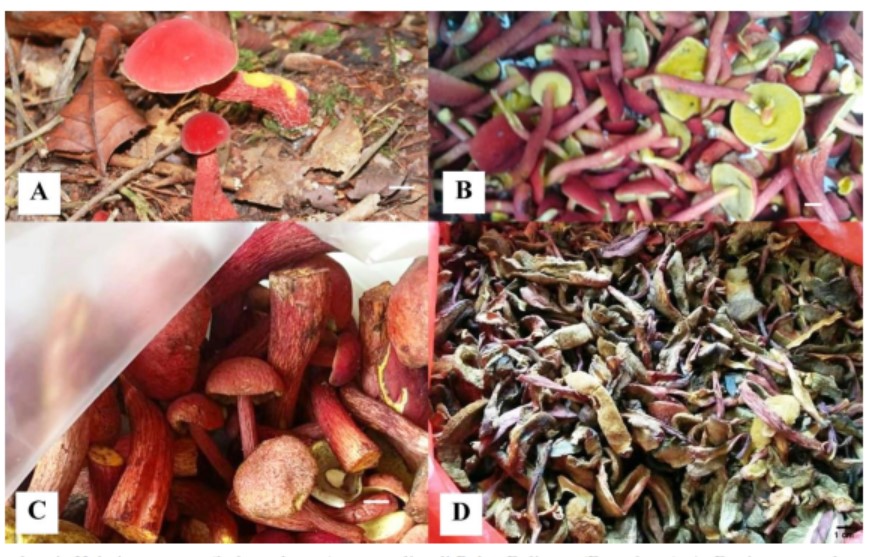
Belitong Island, The Province of Bangka Belitung is one of the exotic places with the biodiversity which has not been optimally inventoried. One of the potential germplasm that has not been recorded properly on Belitong Island is the mushrooms diversity and their potential uses. Mushroom are known as non-timber forestry product that is often sought after by local ethnic of Belitong Island and used as food. Apart from being consumed, these wild mushrooms are also traded, so they are one of the important seasonal commodities for the local community. This research aimed to provide the basic taxonomical information of wild edible mushroom in Belitong island as well as the biological characters. Observations were conducted 2 times in 2018 – 2019 using opportunistic sampling method. The utilization data of wild edible mushroom were collected to complete the macrofungi description in this study. A number of 5 edible wild mushrooms with th economic value reported in this study were: Amanita sect. caesarea (kulat pelandok), Heimioporus sp. (kulat pelawan), Hygrocybe cf. conica (kulat tiong), Phylloporus sp. (kulat sukatan) and Volvariella sp. (kulat sawit). Three species of fungi are ectomycorrhizal forming fungi, namely kulat pelandok with Schima wallichii, kulat pelawan with Tristaniopsis merguensis, and kulat sukatan which host is still unclear. Meanwhile the rest are saprophytic macrofungi. All wild edible mushrooms are members of the phylum Basidiomycota which are divided into 2 orders and 4 families. Heimioporus sp. is known to be the highest selling price mushroom compared to the others, which indicated the potential prospect to proceed to the cultivation stage. In addition, conservation management of plants that are hosts of ectomycorrhizal fungi need to be an important concern on Belitong Island.
Copyright (c) 2020 Jurnal Wasian

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright and License
All articles published in Wasian Journal are the property of the authors. By submitting an article to Wasian Journal, authors agree to the following terms:
-
Copyright Ownership: The author(s) retain copyright and full publishing rights without restrictions. Authors grant the journal the right to publish the work first and to distribute it as open access under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
-
Licensing: Articles published in Wasian Journal are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). This license allows others to share, copy, and redistribute the material in any medium or format, and adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially, provided that proper credit is given to the original author(s) and the source of the material

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. -
Author's Rights: Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges and greater citation of published work.
-
Third-Party Content: If your article contains material (e.g., images, tables, or figures) for which you do not hold copyright, you must obtain permission from the copyright holder to use the material in your article. This permission must include the right for you to grant the journal the rights described above.
-
Reprints and Distribution: Authors have the right to distribute the final published version of their work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), provided that the original publication in Wasian Journal is acknowledged.
For the reader you are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format for any purpose, even commercially.
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit , provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made . You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation .
No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rightsmay limit how you use the material.